

The vaccine is currently recommended for all children and people at risk, including family members of people with hepatitis B. (2013) Exosomes mediate the cell-to-cell transmission of IFN-a-induced antiviral. People who have never been infected with hepatitis B can get a safe, effective vaccine to protect them from getting the infected. 1The mecha- nism by which chronic infection is maintained remains obscured. But for others, the infection becomes chronic, meaning it lasts more than six months. For most people, hepatitis B is short term, also called acute, and lasts less than six months. People who get tested for hepatitis B and find out that they are infected can help protect their family members by encouraging them to get tested for hepatitis B. Overview Hepatitis B is a serious liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). How does getting tested help protect family members? Lifesaving treatments are available to slow down or prevent liver damage, so getting tested helps people access needed medical treatment. Getting tested helps people access medical treatments that can save their lives. Why should people get tested for hepatitis B if they don’t feel sick?Įven though most people with hepatitis B don’t feel sick, liver damage can still occur. People who live with someone who has hepatitis B All medically stable infants weighing 2,000 grams are recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccine within the first 24 hours following birth.

The prevalence of HBV infection in the population was about 60 and the proportion of chronic HBV carriers around 10. How common is Hepatitis B among Asian Americans? Background: Before universal infant immunization against hepatitis B virus (HBV) in 1986 China was a region endemic for HBV infection.
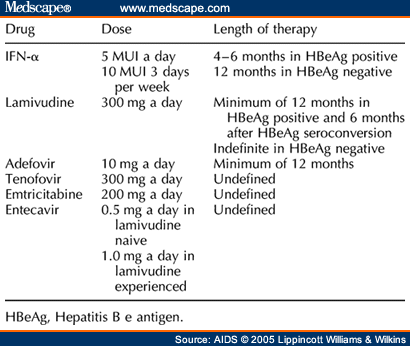
These problems can include liver cancer and liver failure. Hepatitis B can cause serious health problems over time. For some people who get hepatitis B, the virus stays in the body, causing a lifelong illness.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
